
Stefanie Butland, rOpenSci Community Manager Some things are just irresistible to a community manager – PhD student Hugo Gruson’s recent tweets definitely fall into that category.

Stefanie Butland, rOpenSci Community Manager Some things are just irresistible to a community manager – PhD student Hugo Gruson’s recent tweets definitely fall into that category.

In late November 2018, we ran the third annual rOpenSci ozunconf. This is the sibling rOpenSci unconference, held in Australia. We ran the first ozunconf in Brisbane in 2016, and the second in Melbourne in 2017. Photos taken by Ajay from Fotoholics As usual, before the unconf, we started discussion on GitHub issue threads,and the excitement was building with the number of issues.

I never really thought I would write an R package. I use R pretty casually. Then, this year, I was invited to participate during the last week of the Analytical Paleobiology short course, an intensive month-long experience in quantitative paleontology. I was thrilled to be invited.

spatsoc is an R package written by Alec Robitaille, Quinn Webber and Eric Vander Wal of the Wildlife Evolutionary Ecology Lab (WEEL) at Memorial University of Newfoundland. It is the lab’s first R package and was recently accepted through the rOpenSci onboarding process with a big thanks to reviewers Priscilla Minotti and Filipe Teixeira, and editor Lincoln Mullen.
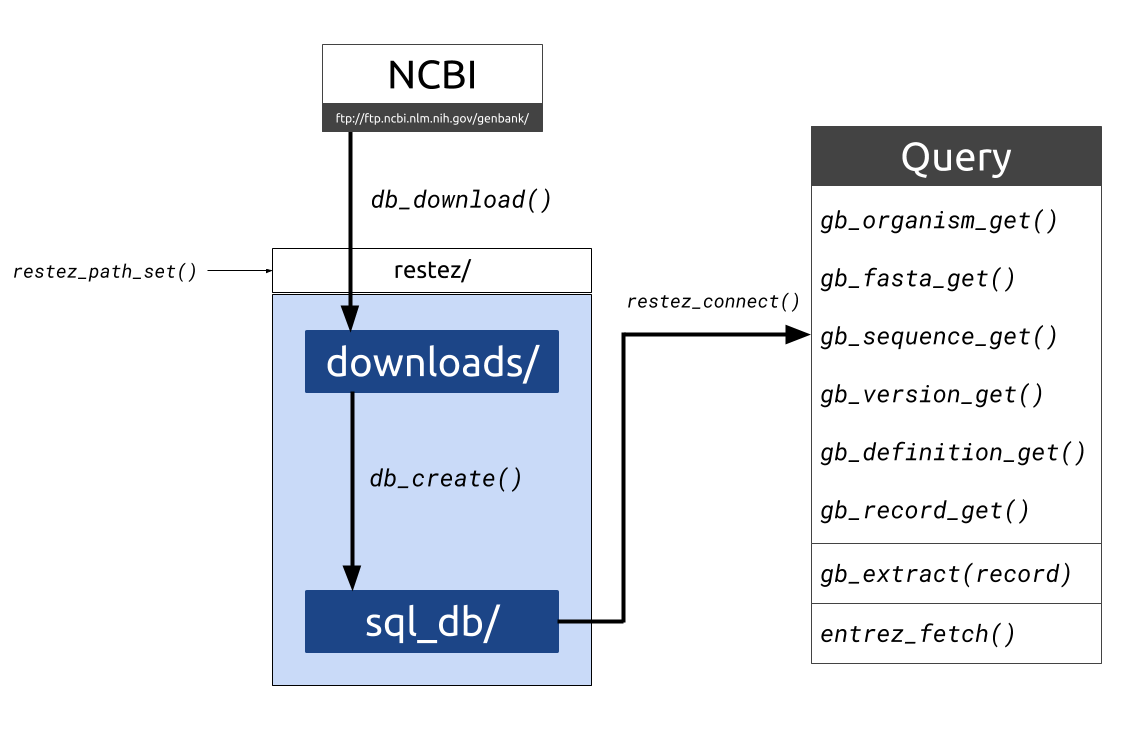
What is restez? R packages for interacting with the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) have, to-date, depended on API query calls via NCBI’s Entrez.For computational analyses that require the automated look-up of reams of biological sequence data, piecemeal querying via bandwith-limited requests is evidently not ideal.
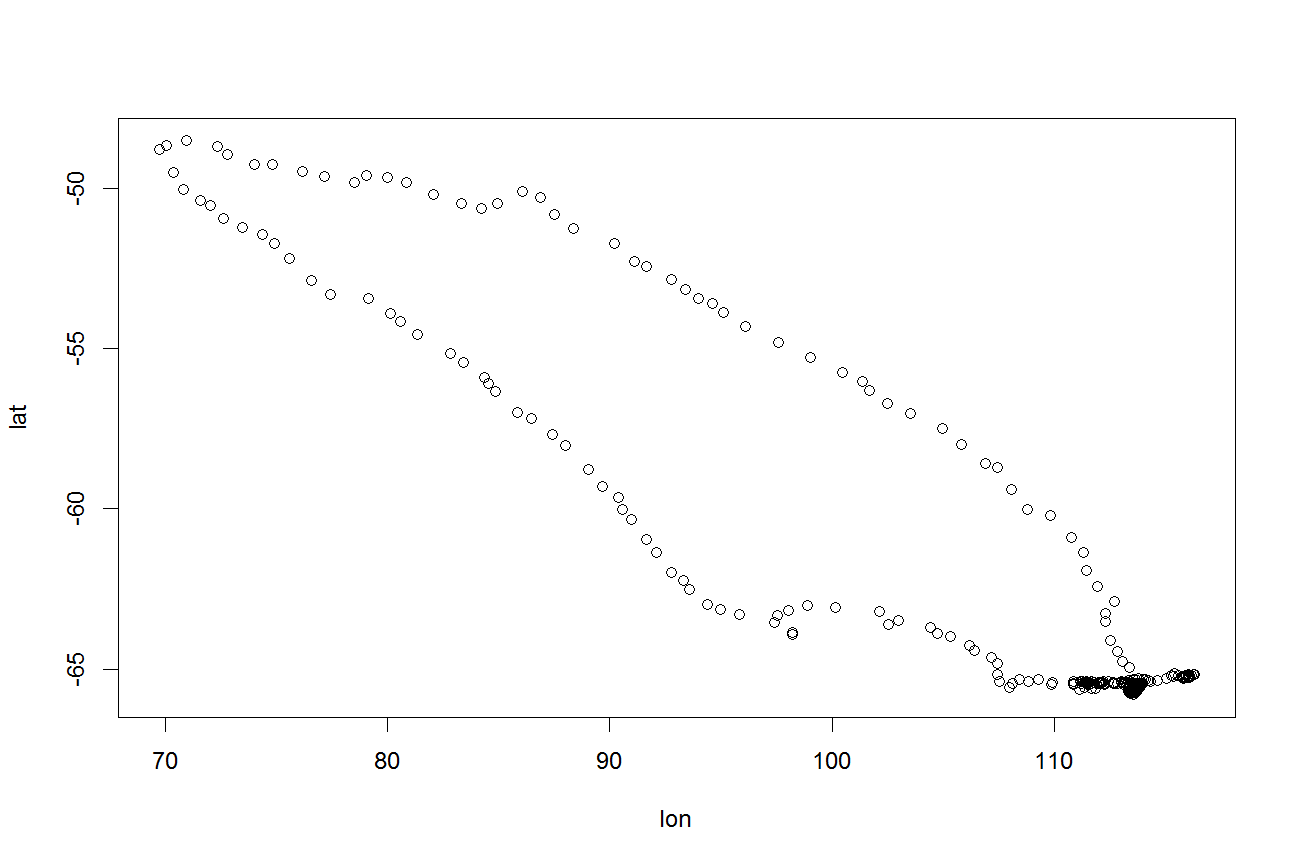

Antarctic/Southern Ocean science and rOpenSci Collaboration and reproducibility are fundamental to Antarctic and Southern Ocean science, and the value of data to Antarctic science has long been promoted. The Antarctic Treaty (which came into force in 1961) included the provision that scientific observations and results from Antarctica should be openly shared.
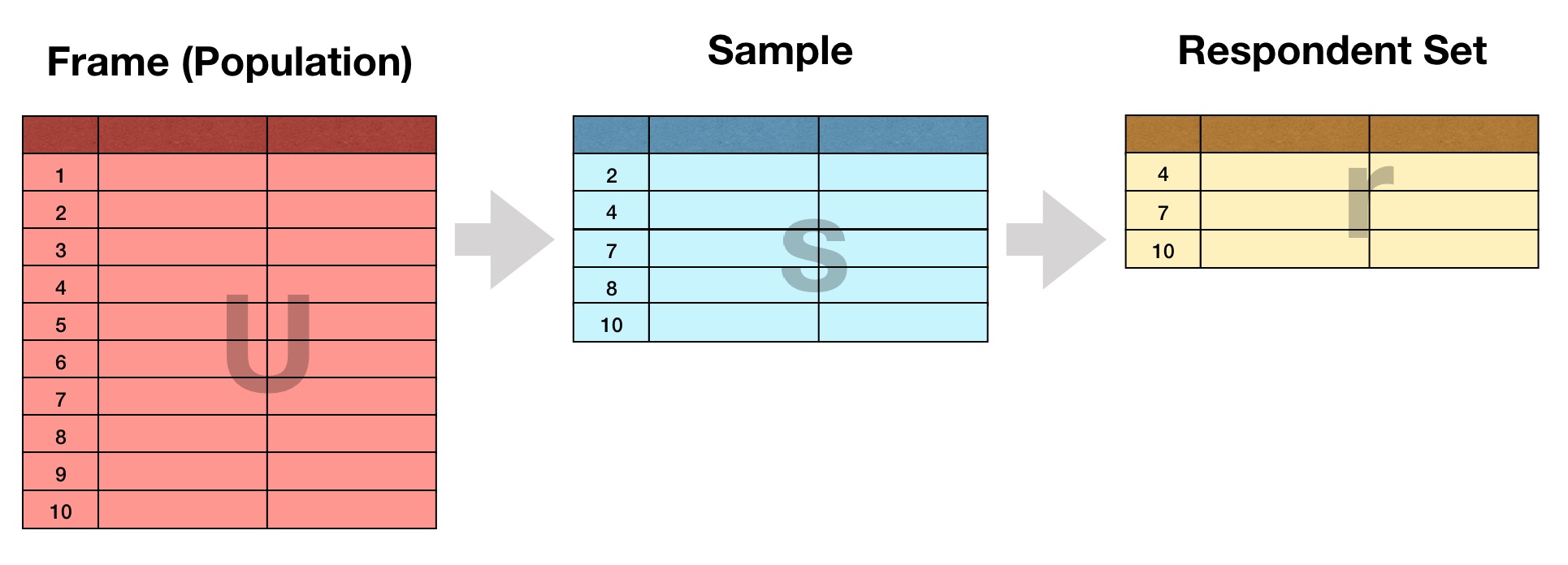
Background Surveys are ubiquitous in the social sciences, and the best of them are meticulously planned out. Statisticians often decide on a sample size based on a theoretical design, and then proceed to inflate this number to account for “sample losses”. This ensures that the desired sample size is achieved, even in the presence of non-response.

I started writing this post back in August, and I hurried it a little because of a Limping Chicken article guest written by researchers at the Deafness, Cognition and Language Research Centre at University College London. I’ve known the DCAL folks for years, and they graciously acknowledged some of my previous writings on this issue.
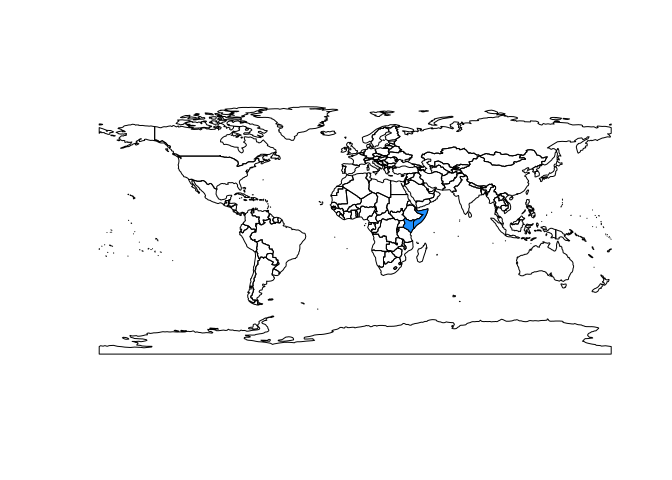
Hundreds of thousands of people in east Africa have been displaced and hundreds have died as a result of torrential rains which ended a drought but saturated soils and engorged rivers, resulting in extreme flooding in 2018.This post will explore these events using the R package smapr, which provides access to global satellite-derived soil moisture data collected by the NASA Soil Moisture Active-Passive (SMAP) mission and abstracts away some of

Sharing data sets for collaboration or publication has always been challenging, but it’s become increasingly problematic as complex and high dimensional data sets have become ubiquitous in the life sciences. Studies are large and time consuming; data collection takes time, data analysis is a moving target, as is the software used to carry it out.