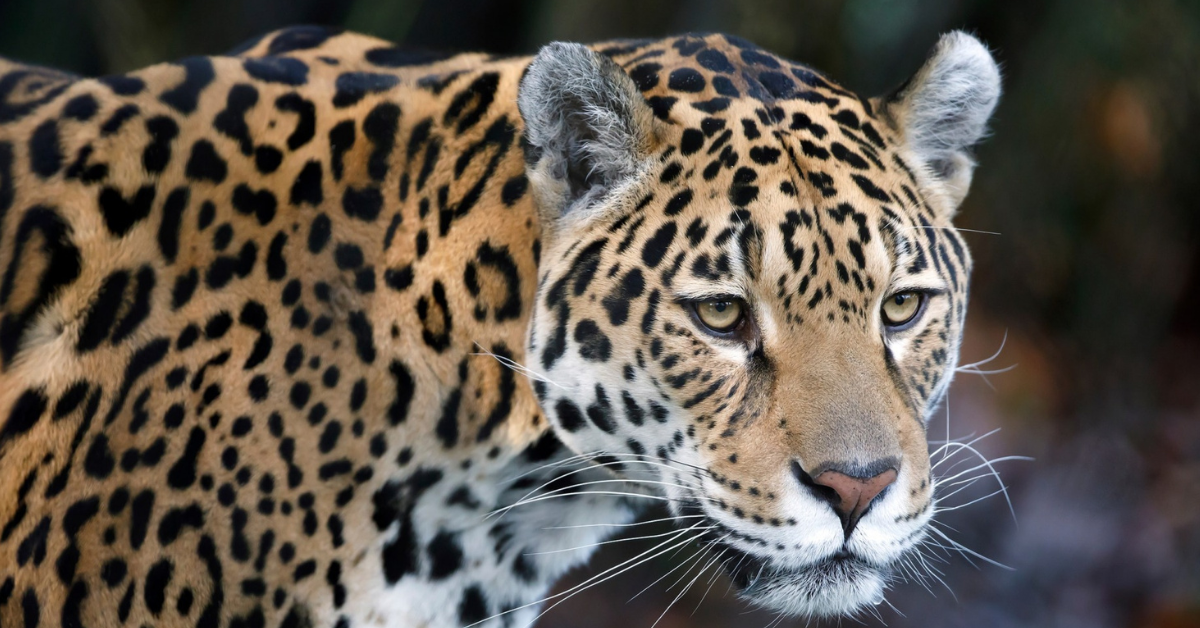

Jaguars are large, solitary, carnivorous mammals belonging to the Felidae family. They are the third largest feline species in the world, after tigers and lions, and are the largest feline species in the Americas.

Jaguars are large, solitary, carnivorous mammals belonging to the Felidae family. They are the third largest feline species in the world, after tigers and lions, and are the largest feline species in the Americas.

Topics covered: I. Background on CheetahImportance of studying cheetah ecology II. Habitat and Distribution Range of cheetahs Habitat requirements Factors affecting habitat suitability III. Diet and Hunting Behavior Prey selection Hunting tactics Competition with other predators IV. Reproduction and Life CycleMating behavior Gestation and birth Development and growth V. Population Dynamics and Conservation VI. Human-Cheetah Interactions VII.
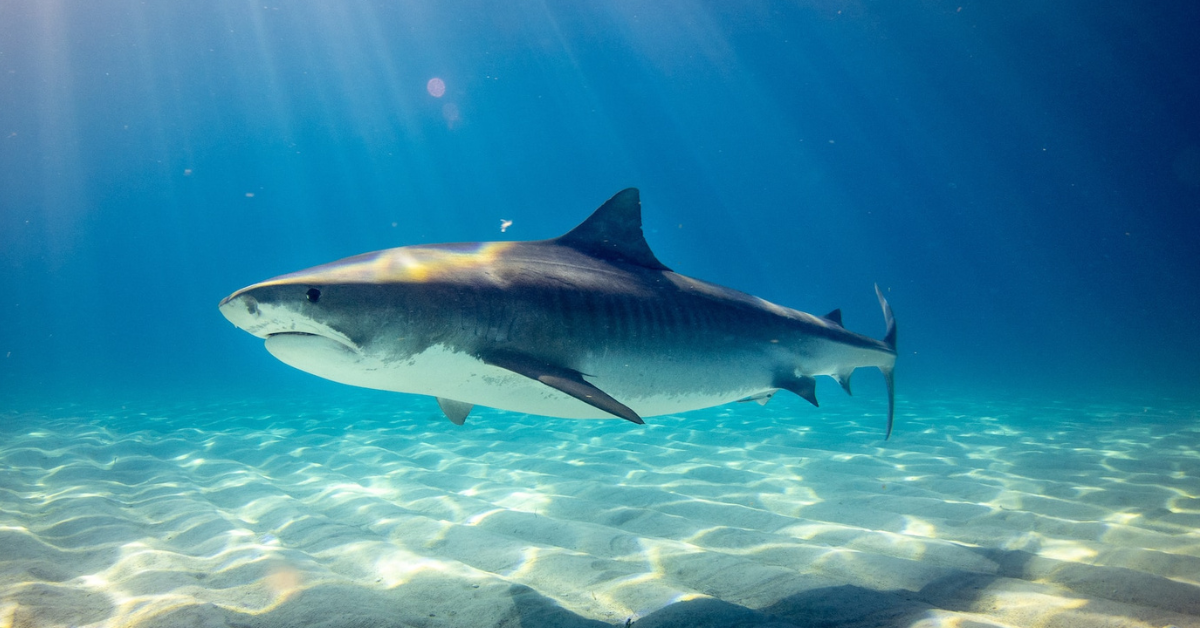

What are sharks? Sharks are a group of cartilaginous fish that have a distinctive body shape, with five to seven gill slits on the sides of their heads and a skeleton made of cartilage instead of bone. There are over 500 different species of sharks that vary greatly in size, color, and behavior.
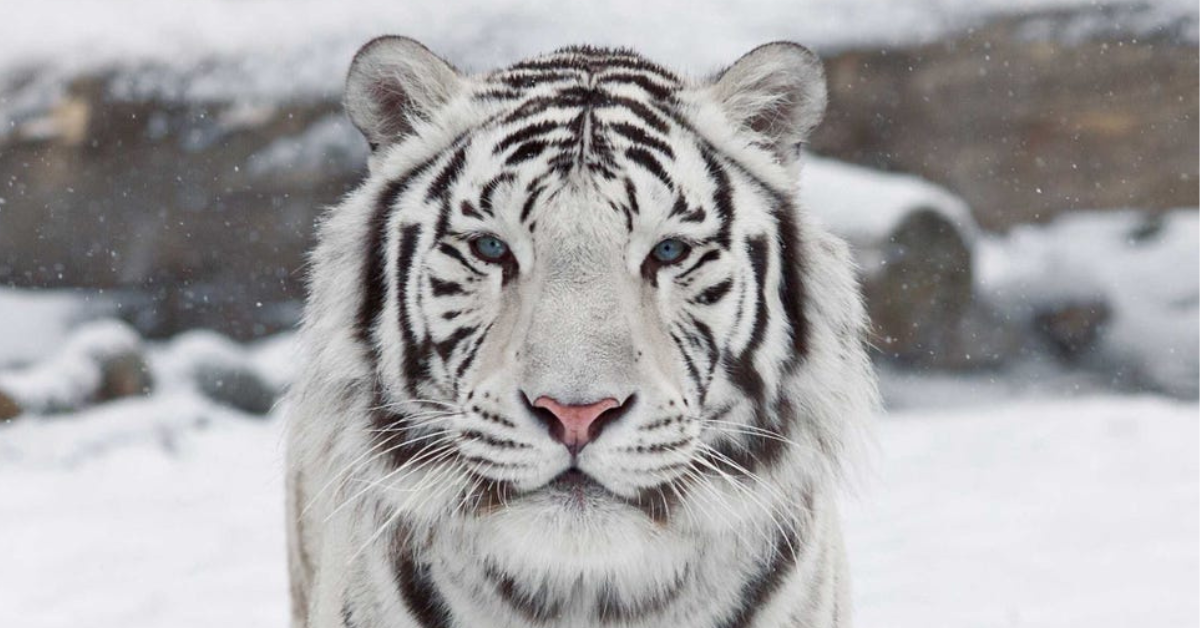

Characteristics of White Tiger The white tiger is a rare and magnificent animal with unique characteristics. Here are some of the most notable features and traits of the white tiger: White fur : The most distinctive feature of the white tiger is its white fur, which is caused by a recessive gene. This fur is usually pale to pure white in color and has black stripes.
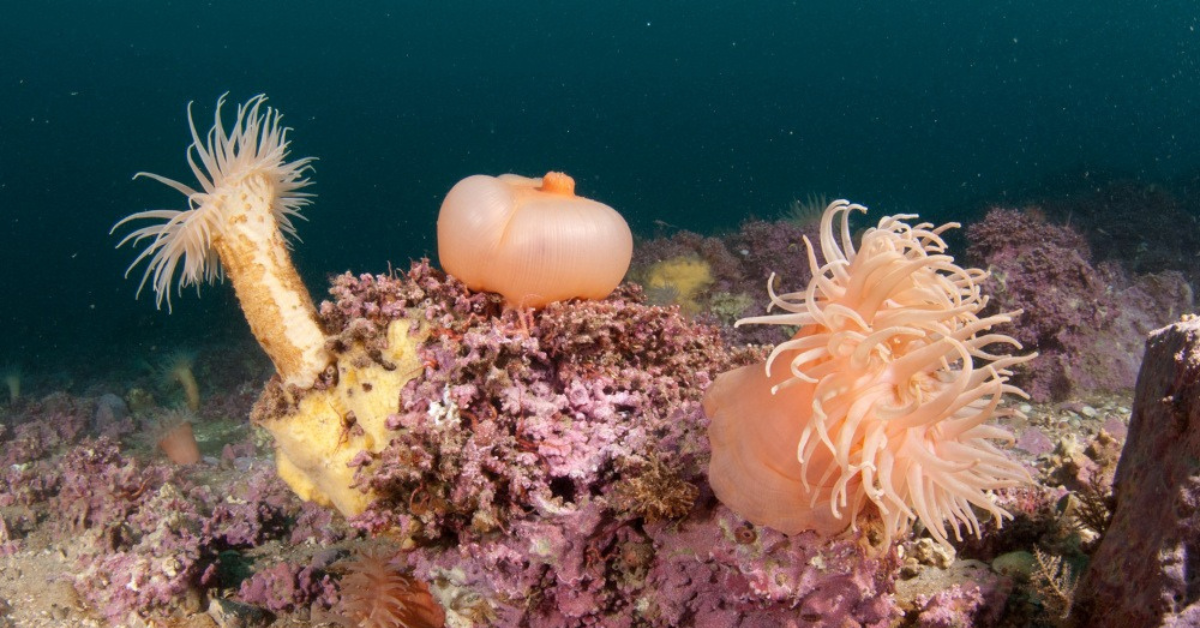

Benthic organisms and their role in ecosystem Benthic organisms are organisms that live on or near the ocean floor, lake or river beds, or other aquatic environments. These organisms are adapted to the benthic zone, which is the lowest level of a body of water where light does not penetrate and the pressure is high.
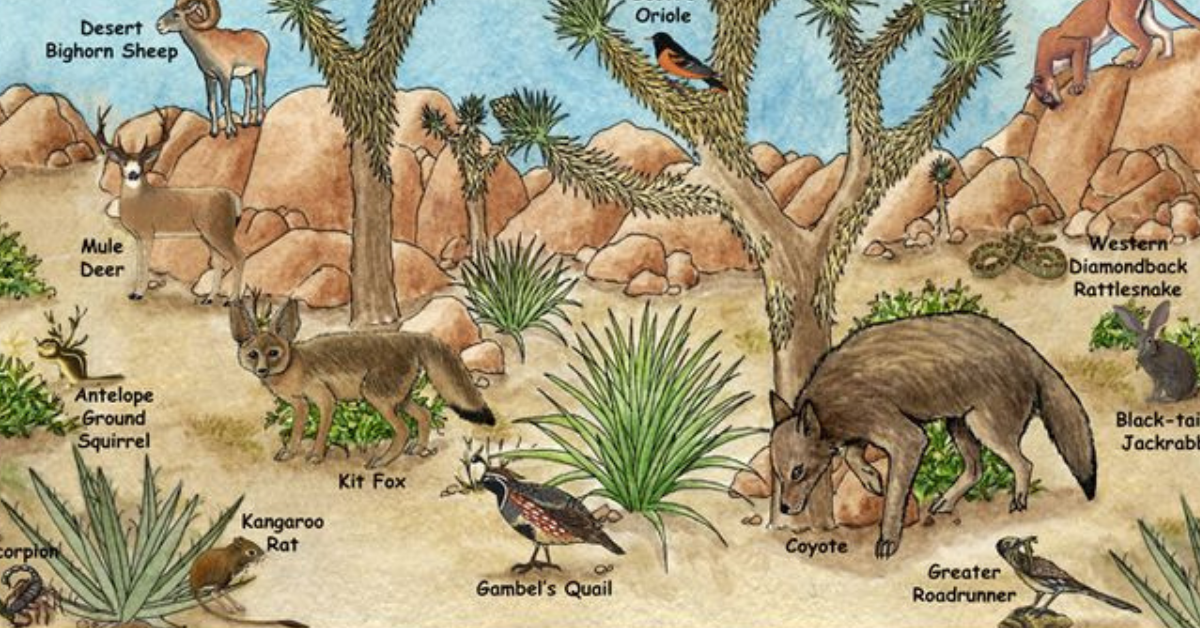
Deserts and their characteristics A desert is a barren, arid region that receives very little precipitation and has a limited amount of vegetation. Deserts can be found in various parts of the world, including Africa, the Middle East, Australia, and North America. The lack of water in the desert makes it a challenging environment for plants and animals to survive, which has led to the development of unique adaptations to the harsh conditions.
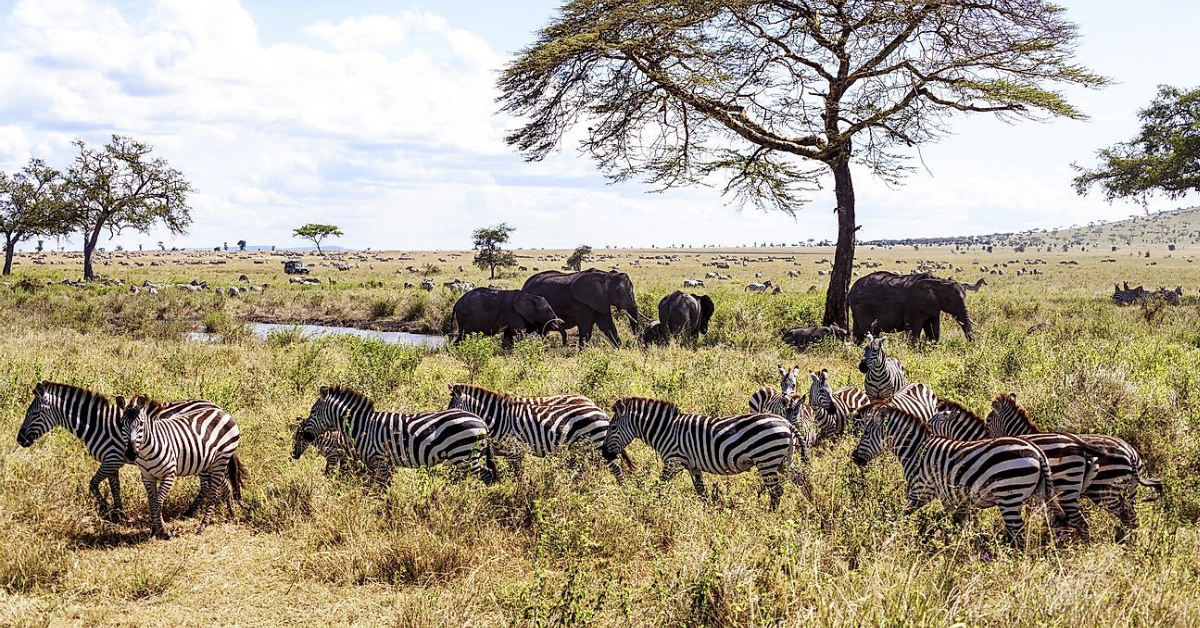

Animals living in grasslands have developed various adaptations that enable them to survive in this environment. Some of these adaptations include: Running : Many grassland animals, such as gazelles, zebras, and antelopes, are fast runners that can outrun predators. They have long, powerful legs that help them run quickly and change direction rapidly.
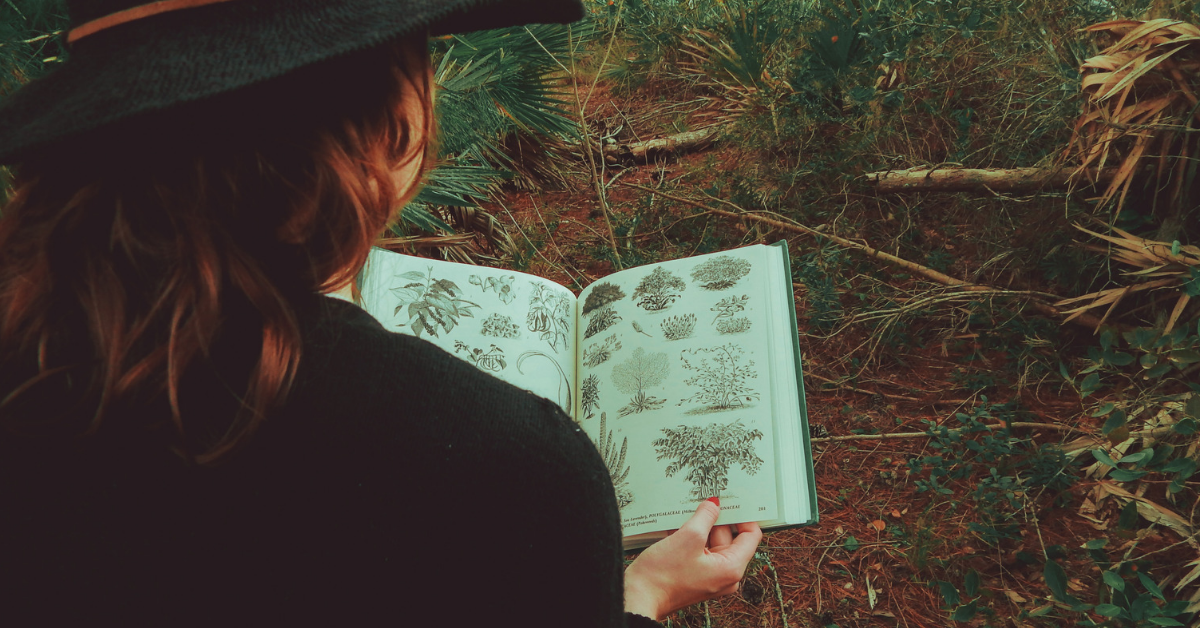

Ecologists study species using a variety of methods, depending on the specific questions they are trying to answer or animal group they are working on. Here are a some common techniques: Field surveys : Ecologists may conduct field surveys to collect data on the distribution and abundance of different species. This can involve visual or auditory surveys, trapping or netting, or sampling of environmental DNA.

Ecologists use a wide variety of tools and techniques to study the natural world and to better understand the interactions between organisms and their environment. Here are some of the most common tools used by ecologists: Field equipment : This includes tools such as binoculars, GPS units, cameras, and sampling equipment (e.g., nets, traps, corers) used to collect data in the field.

How to study animals in the wild? Studying animals in the wild can be a fascinating and rewarding experience, but it can also be challenging. Here are some steps you can take to study animals in their natural habitat:Choose your study site: Select an area where the animals you want to study can be found. This could be a national park, wildlife refuge, or other natural area.