Cyclopropenylidene must be the smallest molecule to be aromatic due to π-electrons, with just three carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms. It has now been detected in the atmosphere of Titan, one of Saturn’s moons[cite]10.3847/1538-3881/abb679[/cite] and joins benzene, another aromatic molecule together with the protonated version of cyclopropenylidene, C 3 H 3 + also found there.
Messaggi di Rogue Scholar
Way back in 2010, I was writing about an experience I had just had during an organic chemistry tutorial, which morphed into speculation as to whether a carbon atom might sustain a quadruple bond to nitrogen. A decade on, and possibly approaching 100 articles by many authors on the topic, quadruple bonds to carbon continue to fascinate.
The title of this post indicates the exciting prospect that a method of producing a room temperature superconductor has finally been achived[cite]10.1038/s41586-020-2801-z[/cite]. This is only possible at enormous pressures however; >267 gigaPascals (GPa) or 2,635,023 atmospheres.
Here I investigate a recent report[cite]10.1126/sciadv.abc0495[/cite] of a new generation of polyesters with the intrinsic properties of high crystallinity and chemical recyclability. The latter point is key, since many current plastics cannot be easily recycled to a form which can be used to regenerate the original polymer with high yield. Here I show some aspects of this fascinating new type of polymer.
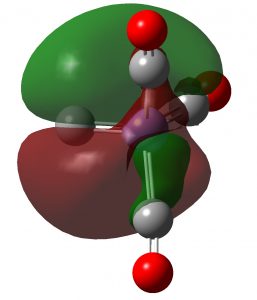
Sometimes a (scientific) thought just pops into one’s mind. Most are probably best not shared with anyone, but since its the summer silly season, I thought I might with this one. Famously, according to Einstein, m = E/c^^2, the equivalence of energy to mass. Consider a typical exoenergic chemical reaction: A → B, ΔG -100 kJ/mol.
Metaldehyde is an insecticide used to control slugs.
I occasionally notice that posts that first appeared here many years ago suddenly attract attention.
A little more than a year ago, a ChemRxiv pre-print appeared bearing the title referenced in this post,[cite]10.26434/chemrxiv.8009633.v1[/cite] which immediately piqued my curiosity. The report presented persuasive evidence, in the form of trapping experiments, that dicarbon or C 2 had been formed by the following chemical synthesis.
In the news this week is a report of a molecule whose crystal lattice is capable of both storing and releasing large amounts of hydrogen gas at modest pressures and temperatures. Thus “NU-1501-Al” can absorb 14 weight% of hydrogen. To power a low-polluting car with a 500 km range, about 4-5 kg of hydrogen gas would be need to be stored and released safely.
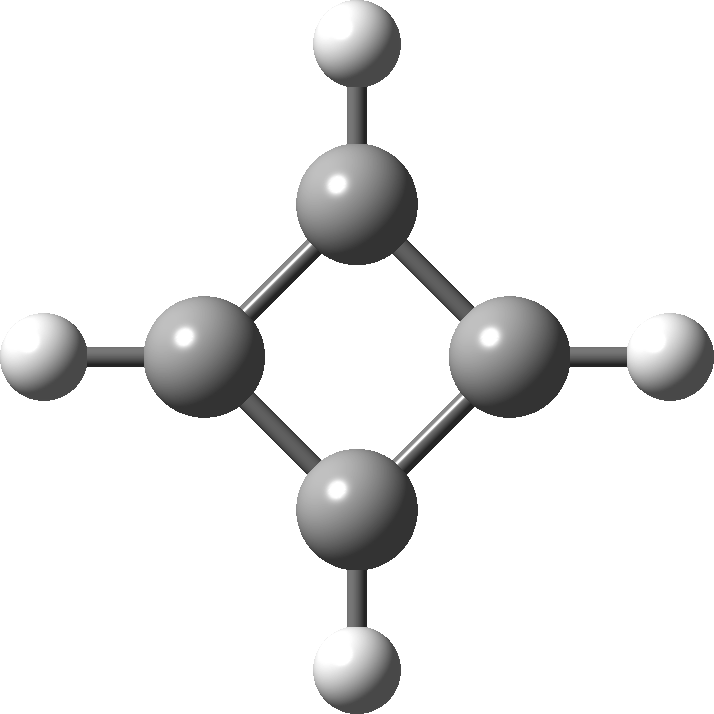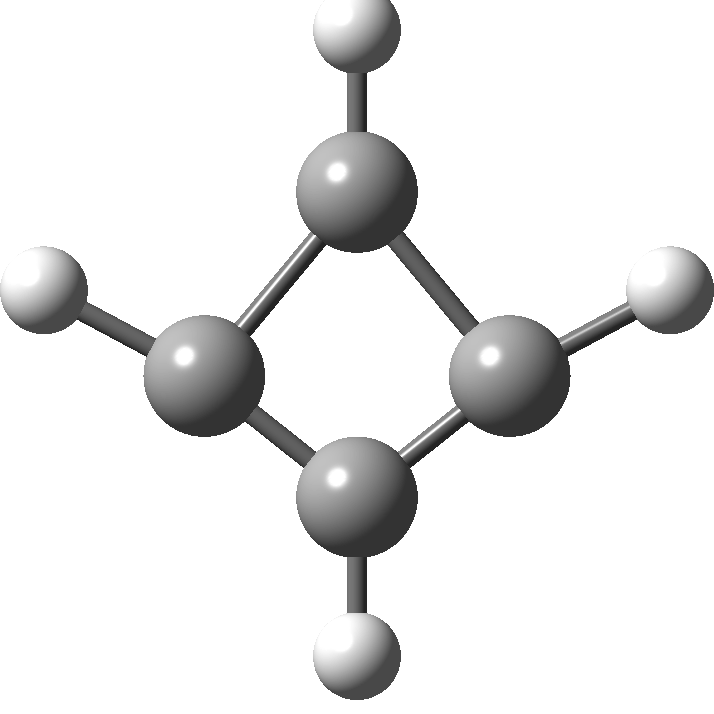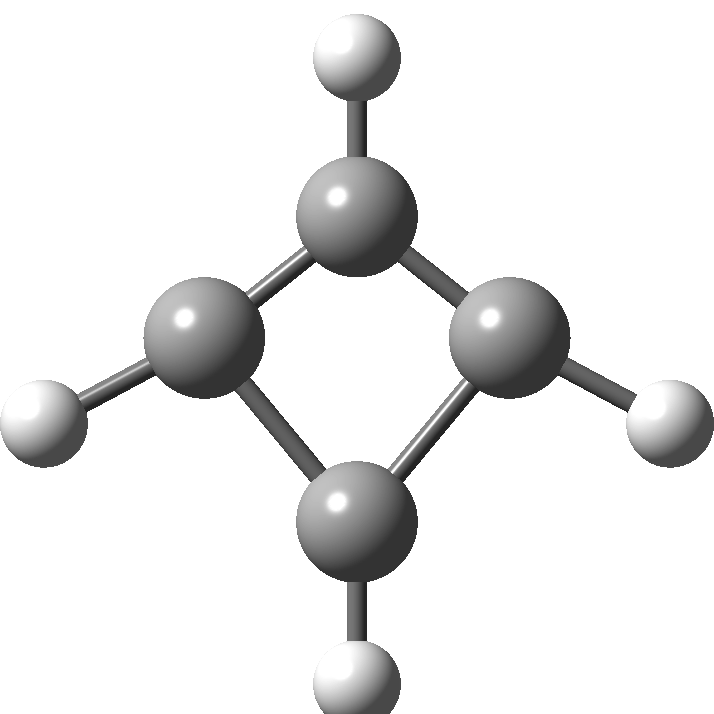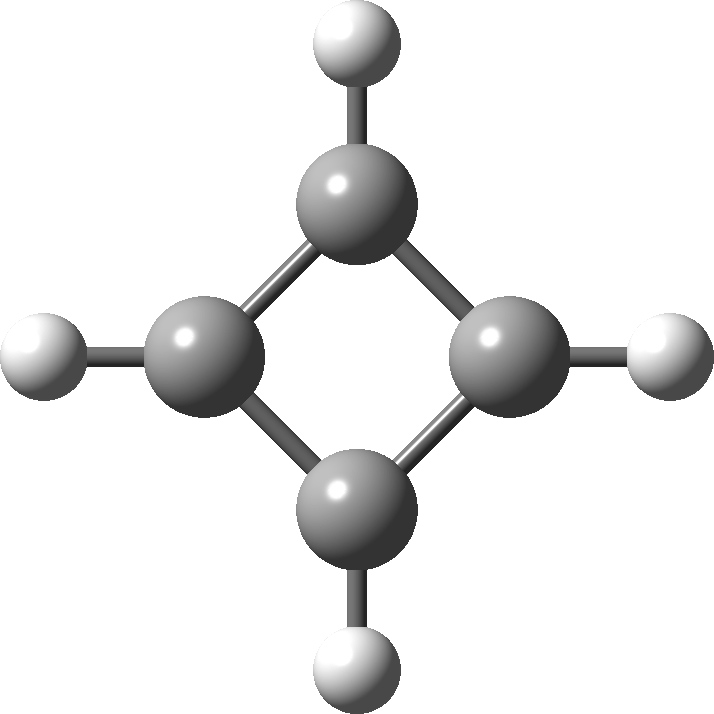
In 2001, Shaik and co-workers published the first of several famous review articles on the topic A Different Story of π-Delocalization.